About Malnutrition
Malnutrition is a condition caused by poor nutrition, and can manifest as undernutrition, overnutrition, or micronutrient deficiencies.5
- Undernutrition is caused by insufficient intake of energy, protein, or essential nutrients, leading to weight loss. Malnutrition from undernutrition negatively impacts functional status parameters, activities of daily living, muscle mass and strength, frailty, sarcopenia, risk of falls, and immune function.9-14
- Overnutrition involves excessive caloric intake, often leading to obesity and related metabolic disorders.
- Micronutrient deficiencies occur when an individual has inadequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals in their diet, potentially resulting in health complications
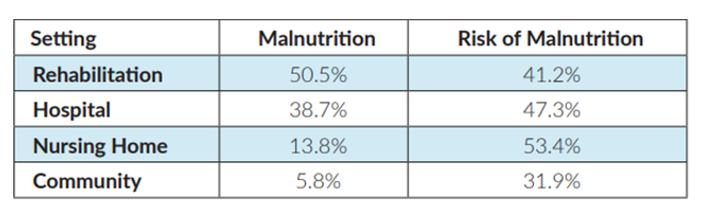
Malnutrition exists in both institutional care and the community.6
A large-scale multinational study showed that malnutrition in adults 65 years and older remained high across all care settings:15
Malnutrition also affects individuals living in the community, particularly among those who are socioeconomically disadvantaged or experiencing food insecurity. Limited access to nutritious food, poor dietary habits, and inadequate nutritional knowledge can contribute to malnutrition within the broader community.16
CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES OF MALNUTRITION
Malnutrition is both a cause and consequence of disease.
As a cause of disease, malnutrition weakens the body's immune system and compromises its ability to fight off infections and recover from illnesses. Insufficient intake of essential nutrients, particularly protein, vitamins, and minerals, can lead to decreased muscle mass and strength, impaired organ function, and delayed wound healing.6
Conversely, many medical conditions and chronic diseases can lead to a loss of appetite, malabsorption of nutrients, or increased energy expenditure. These factors can result in unintended weight loss, nutrient deficiencies, and muscle wasting. Moreover, medical treatments like chemotherapy or surgery can cause side effects that further contribute to malnutrition.6
CONDITIONS ASSOCIATED WITH MALNUTRITION
Malnutrition is often linked to numerous medical conditions, including:
- Chronic diseases: Cancer, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and inflammatory bowel disease can contribute to malnutrition due to increased metabolic demands or decreased appetite.
- Malabsorptive disorders: Conditions like celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and short bowel syndrome hinder nutrient absorption, and may lead to malnutrition.
- Eating disorders: Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder can result in malnutrition and significant health consequences.
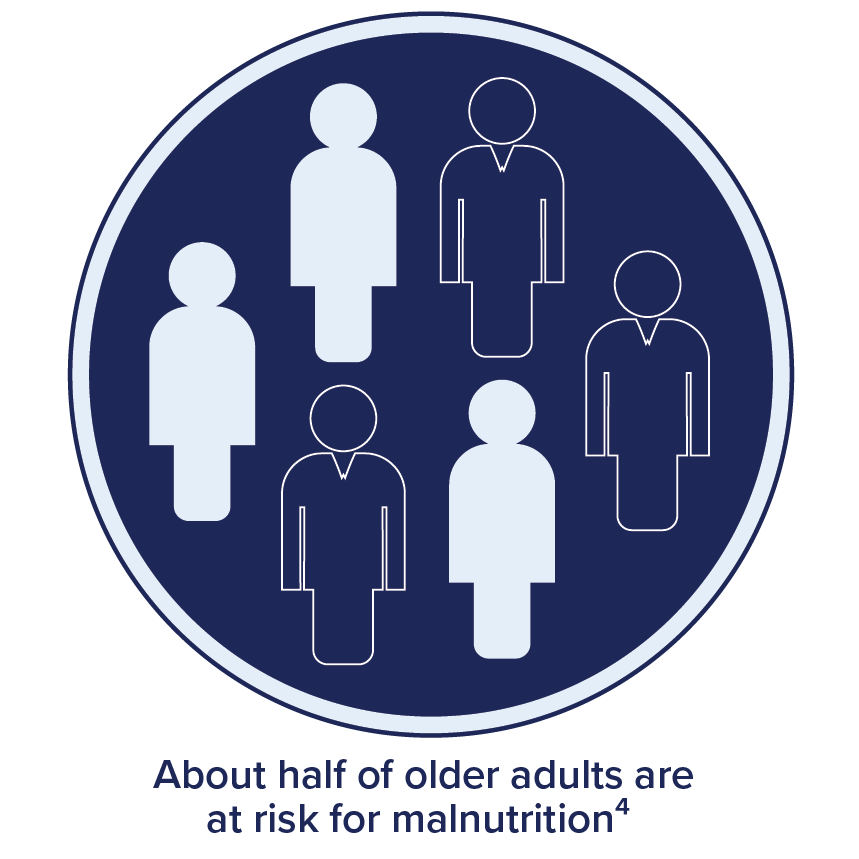
Aging Increases Risk of Malnutrition:
- Risk of malnutrition increases in the elderly, affecting as many as 69% of individuals across different care settings and 30% in the community.15
- Although protein needs increase with age for both healthy and non-healthy older adults to maintain muscle mass and functionality,17,18 more than 40% of adults ages 51 and older are not meeting minimum daily protein requirements.19
Addressing malnutrition requires a holistic approach that considers both the prevention and treatment of malnutrition in diverse settings. Nutritional screening, early intervention, and personalized nutritional support are essential to addressing malnutrition and improving overall health and well-being.21
Nutrition & Malnutrition
NUTRITION STRATEGIES FOR TREATING & PREVENTING MALNUTRITION
Nutrition plays a central role in replenishing depleted nutrients, supporting tissue repair, and restoring the overall health of malnourished patients. Adequate nutrition is essential for the body's immune system, energy metabolism, and organ function. In malnourished individuals, nutrient deficiencies can weaken the immune response, impair wound healing, and lead to muscle wasting, making them more susceptible to infections and other health complications.6 Providing the right nutrients in proper quantities is critical to treat malnutrition and promote optimal recovery.
Early intervention and appropriate nutrition management are key strategies in treating and preventing malnutrition.7
Various nutrition interventions, including nutrition counseling, oral nutritional supplements, vitamin and mineral supplements or enteral nutrition (tube feeding) can be considered in addressing nutrient deficiencies and promoting improved health outcomes for patients at risk or suffering from malnutrition.
Nestlé Health Science's evidence-based nutritional solutions offer a diverse range of options to support healthcare professionals in their efforts to combat malnutrition effectively.
Support Resources
You must be logged in to view all resources.
21 Evidence Found
37 Tools and Product Support Found
5 Patient Resources Found
32 Videos
References
1. https://www.modernhealthcare.com/article/20160923/NEWS/160929940/malnutrition-causes-15-5-billion-in-healthcare-spending-per-year
2. Fingar KR et al. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. 2016; Statistical Brief #218.
3. Goates S et al. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0161833.
4. Snider JT et al. JPEN. 2014;38(2 Suppl):77S-85S.
5. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malnutrition
6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4951875/
7. Eckert KF, Cahill LE. Malnutrition in Canadian hospitals. CMAJ 2018;190:E1207.
8. Snider JT et al. JPEN. 2014;38(2 Suppl):77S-85S.
9. Dehghankar L et al. Biotech Health Sci. 2016;3:e34470.
10. Pierik VD, et al. BMC Geriatrics. 2017;17:118.
11. Liguori I et al. Nutr Clin Pract. 2018;33:879-886.
12. Dorner TE et al. J Nutr Health Aging. 2014;18:264-269.
13. Jacobsen EL et al. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e011512.
14. Neyens J et al. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2013;56:265-269.
15. Kaiser MJ et al. J Am Ger Soc. 2010; 58:1734-1738.
16. Malnutrition: Definition, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment (clevelandclinic.org)
17. Bauer J et al. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013;14:542-559.
18. Deutz NEP et al. Clin Nutr. 2014; 33:929-936.
19. Krok-Schoen J et al. J Nutr Aging. 2019; Feb 19 (Epub ahead of print).
20. Cawood AL et al. Ageing Res Rev. 2012;11:278-296.
21. Donini, Lorenzo M., et al. J Nutr Health Aging vol. 17, no. 1, 2012; 9-15.