About Healthy Aging
Americans are living longer, which is great, but of equal or greater importance is aging healthfully and maintaining one’s quality of life well into their golden years. Given most adults ages 65 and older have at least one chronic disease that may require careful monitoring of diet and nutrient intake, healthy aging and good nutrition go hand-in-hand.1
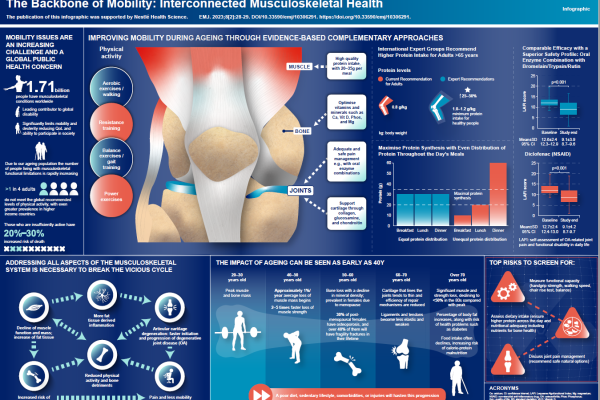
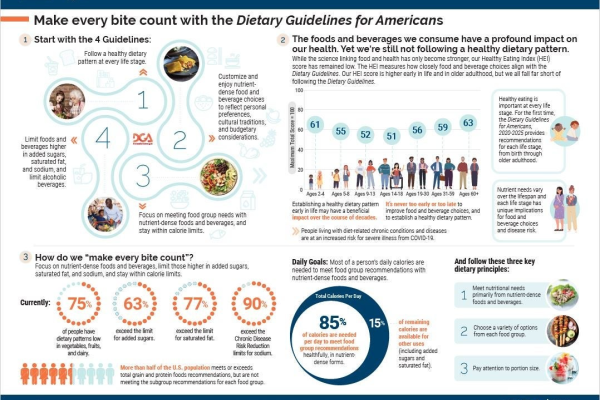
Healthy aging starts with a strong foundation – that is, a lifetime of good eating habits, ample physical activity, and smart lifestyle choices like refraining from smoking and using sunscreen. However, even the most well-built structure wears down over time. Inevitably the foundation will crack, but the key is to reinforce it with good nutrition and healthy choices before it becomes structurally weak. For example, sufficient protein can help combat muscle decline, while calcium and vitamin D continue to be important to mitigate bone density loss.
As older adults tend to have multiple comorbidities, their nutrition needs may grow more complex with age as well. Many health conditions, including type 2 diabetes or certain types of cancer, grow more likely with age. Additionally, many older adults report difficulty with mobility which can lead to frailty and further complications. That’s why healthy aging solutions such as changes in nutrition, activity and overall patient care should be comprehensive and meet a wide range of needs.
Nutrition & Healthy Aging
Determining a patient’s nutrition needs based on their overall lifestyle can be its own challenge. Overlay that with potential issues like decreased appetite, increased need for protein and specific nutrients, and nutrition recommendations for people with chronic conditions such as Type 2 diabetes, and providing tailored medical nutrition therapy can become a complex puzzle.
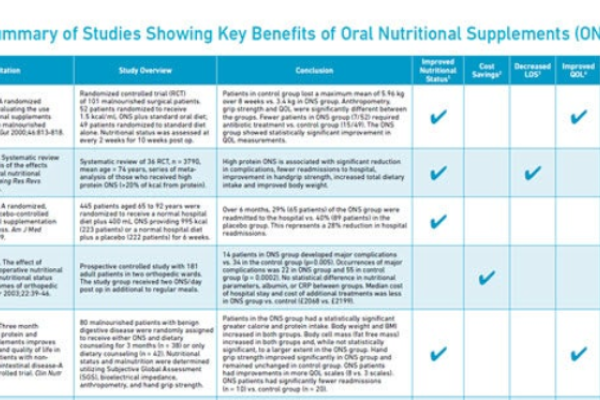
However, this is a common scenario for healthcare providers looking to help older adults manage chronic conditions, maintain their vitality and avoid hospital admissions or lengthy hospital stays. Despite the fact that American adults are living longer, many are living with serious chronic conditions that affect overall health. For example, 1 in 7 adults in North America is living with diabetes,3 and nearly half of older adults are at risk for malnutrition.4
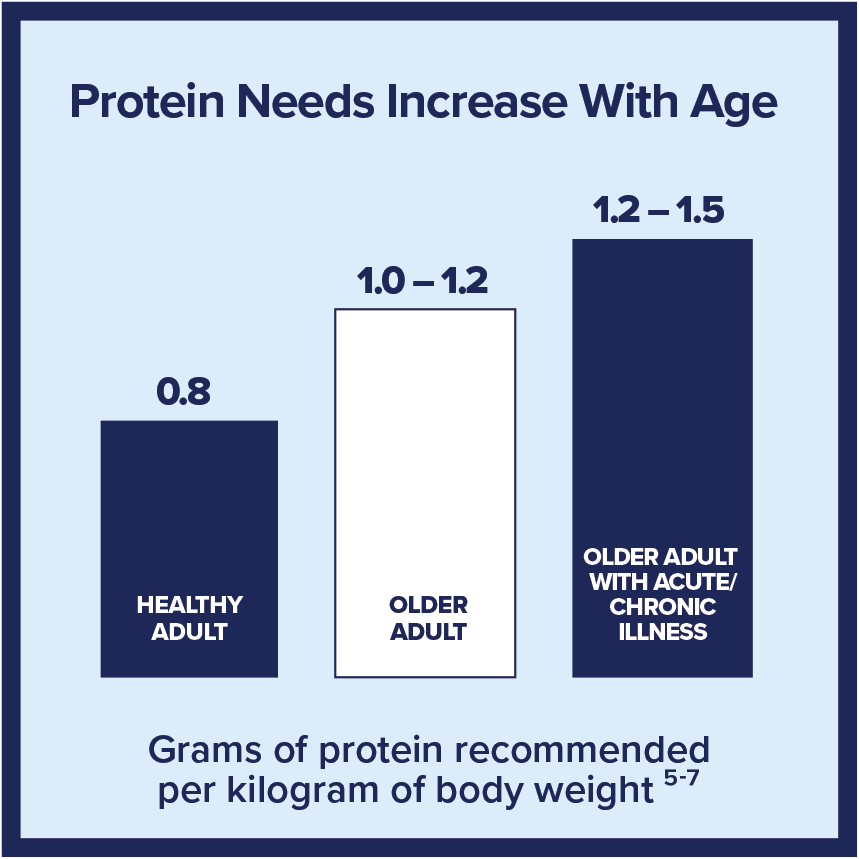
Protein is of particular importance among older adults, 2 as it helps maintain muscle mass, prevent frailty, and supports recovery from illness. Whereas the average adult needs 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, older adults may need 1.0-1.2 grams per kilogram body weight – and even more if they’re severely ill or malnourished.5,6,7 If protein needs are not met, older adults have a greater risk of sarcopenia, frailty and disability.
Additionally, though older adults typically need fewer daily calories than younger adults, many are still not getting enough. This is especially true when older patients are hospitalized. Protein-calorie malnutrition is common among older adults and is associated with longer hospital stays and greater mortality risk.4
Older adults are also more likely to be dehydrated, since the sense of thirst tends to diminish with age. 2 Providing older adults with protein-containing, nutrient-rich beverages allows them to better meet calorie, protein, and vitamin/mineral needs that help support healthy aging.
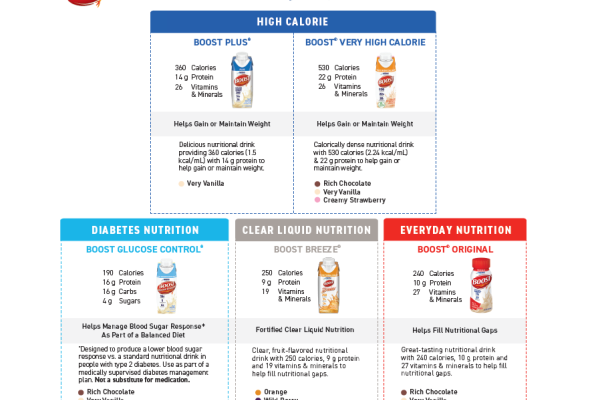
Nestlé Health Science has a wide array of protein- and calorie-dense beverages and powders that help older adults meet their nutrient needs, including those on special diets such as those managing diabetes. All products are designed by nutrition experts with formulations backed by science, and many are brands widely used in healthcare settings.
Support Resources
You must be logged in to view all resources.
8 Evidence Found
18 Tools and Product Support Found
7 Patient Resources Found
12 Videos
References
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living. 2021 Profile of Older Americans. November 2022.
- DeSilva D and Anderson-Villaluz D. Nutrition as We Age: Healthy Eating with the Dietary Guidelines. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Last Updated June 8, 2022.
- International Diabetes Federation, IDF Diabetes Atlas: https://diabetesatlas.org/.
- Defeat Malnutrition Today infographic, 2019. https://defeatmalnutrition.today/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/DMT_Malnutrition_Info_Graphic_OnePage_Update_2.pdf
- Deutz NEP, Bauer JM, Barazzoni R, et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clinical Nutrition. 2014: 929-936. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2014.04.007
- Nutrition Needs for Older Adults: Protein. The National Resource Center on Nutrition & Aging. Updated February 14, 2020.
- Bauer J, Biolo G, Cederholm T, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. JAMDA 14. 2013: 542-559. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2013.05.021