About Cerebral Palsy (CP)
The International Executive Committee for the Definition of Cerebral Palsy defines cerebral palsy as: “a group of permanent disorders of the development of movement and posture, causing activity limitation, that are attributed to non-progressive disturbances that occurred in the developing fetal or infant brain. The motor disorders of cerebral palsy are often accompanied by disturbances of sensation, perception, cognition, communication and behavior, by epilepsy, and by secondary musculoskeletal problems.” 2
There are many different types of CP, which vary in the parts of the body that are affected, the type of impairment and the severity of mobility limitations.
Nutrition & Cerebral Palsy (CP)
Providing optimal nutrition to individuals with cerebral palsy (CP) helps improve their nutritional status and their overall general health.
Quite often, individuals with CP require specific nutritional interventions. Indicators that can help determine if the individual needs nutritional intervention include:
- No weight gain or growth
- A deviation from an established “growth pattern”
- Low body fat-stores with low weight in respect to height or length
- Prolonged or stressful oral feeding
- Signs of pulmonary aspiration or dehydration
- Evidence of micronutrient deficiencies
The choice of a nutritional strategy, as well as the mode of administration, depends on:
- The individual's nutritional status
- The individual's nutritional requirements
- The individual's ability to consume enough food and fluids orally
- The risk of pulmonary aspiration
Before recommending a nutritional strategy, nutritional requirements need to be carefully assessed, as they vary greatly depending on physical impairments, feeding difficulties, body composition and physical activity levels.
Nutritional Strategies for Cerebral Palsy (CP)
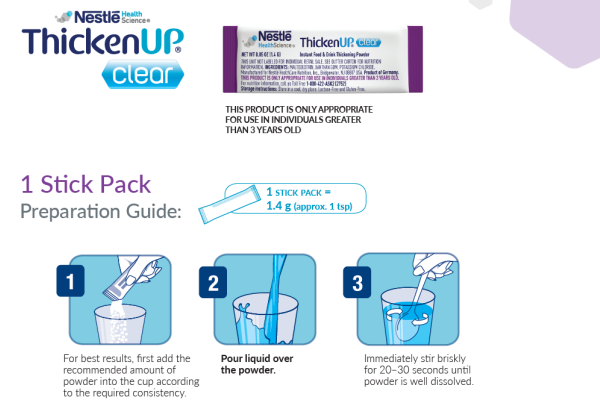
There are several different types of nutritional solutions that may be appropriate for supporting an individual with CP. Introducing thickeners or oral nutritional supplements (ONS), while ensuring adequate composition, positioning and physical support during meals, is usually the first approach. If the individual is not gaining weight with these interventions, then tube feeding may be an appropriate next step.
See below for more information on each nutritional strategy.
Support Resources
You must be logged in to view all resources.
7 Evidence Found
6 Tools and Product Support Found
1 Patient Resources Found
2 Videos
References
1. Cerebral Palsy News Today. "Cerebral Palsy and Diet." https://cerebralpalsynewstoday.com/cerebral-palsy-and-diet/. Accessed 8 Aug, 2022.
2. Colver A et al. Cerebral palsy. Lancet. 2014;383:1240-49.