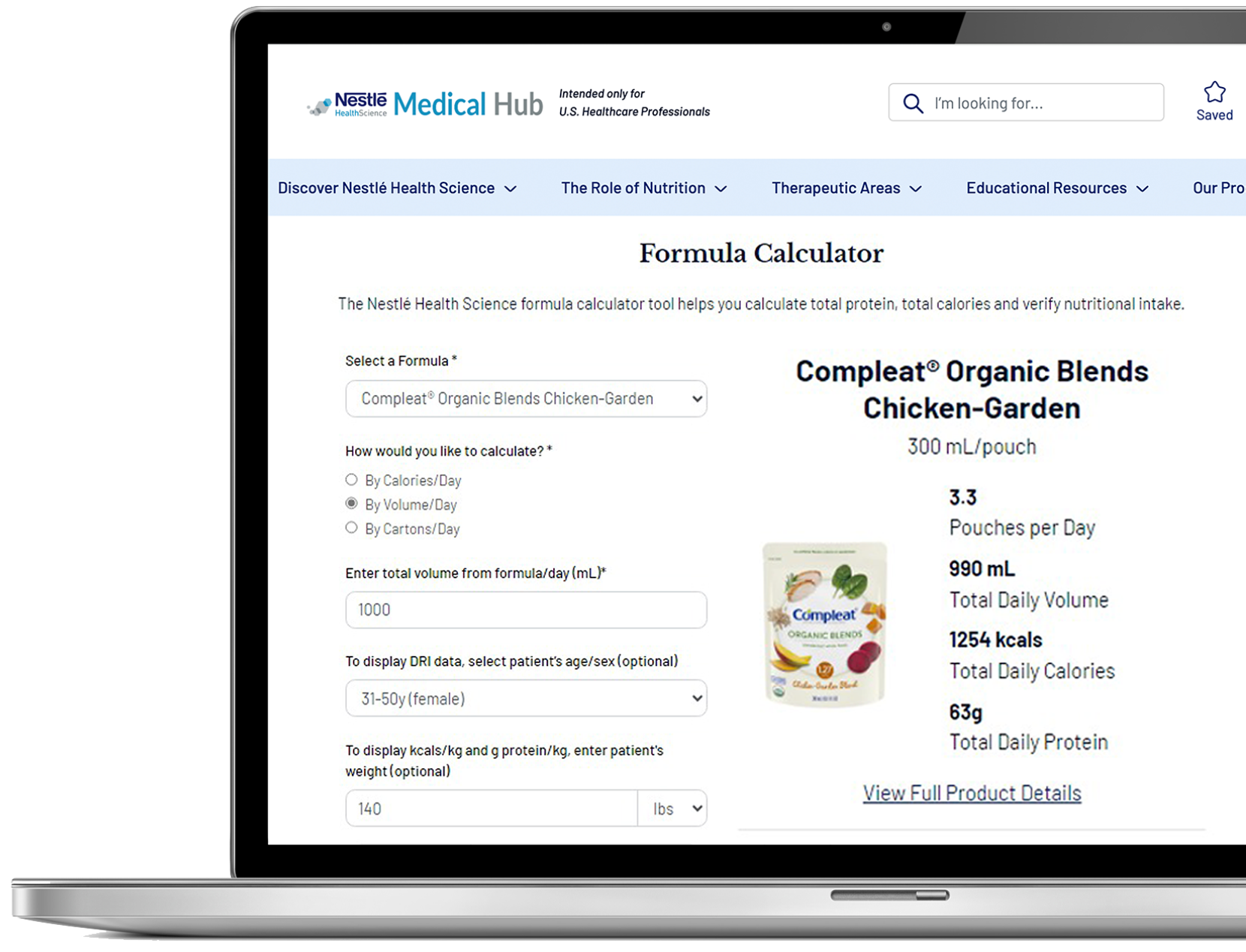
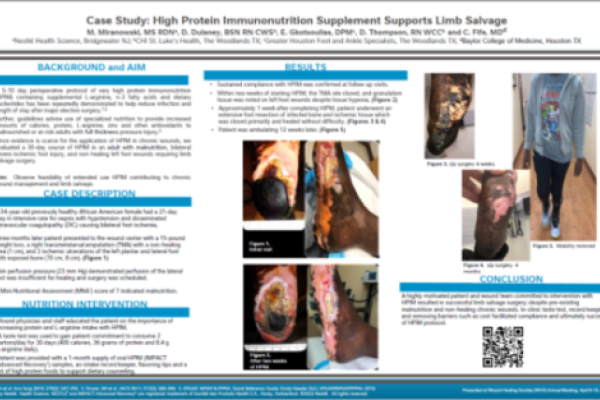
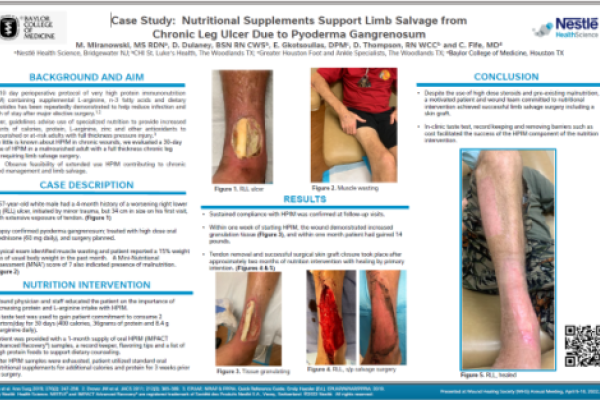
Nutrition & Wounds
The process of wound healing is a metabolically demanding process. Give your at risk patients or those with existing pressure injuries the specialized nutrition they need. This may include:
- Adequate calories—Approximately 30 to 35 kcal/kg/day
- High protein—Approximately 1.25 to 1.5 g protein/kg/day
- Vitamins and minerals—Supplements should be given when deficiencies are demonstrated or suspected
- Adequate fluid—1 mL/kcal (adjust as needed)
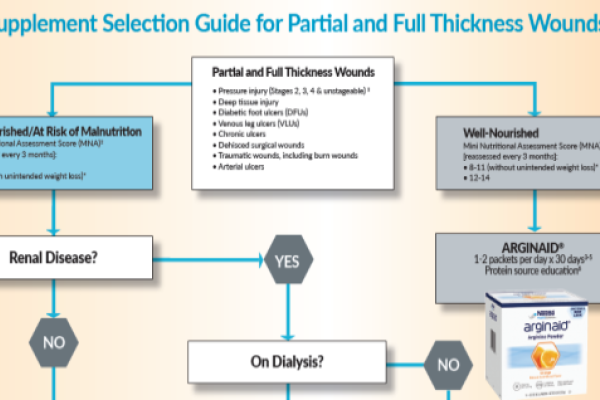
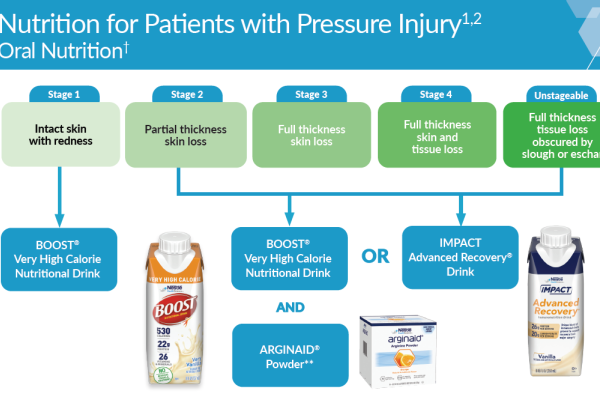
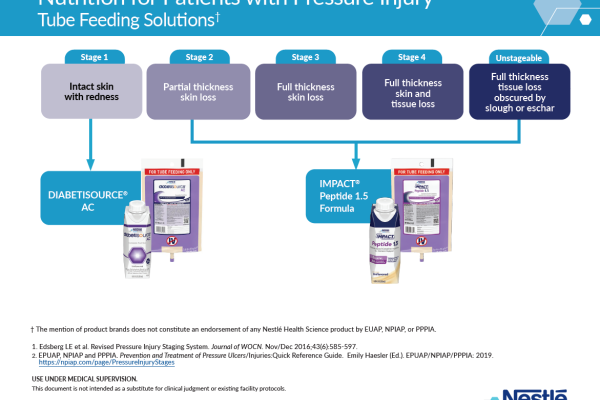
- Supplemental L-arginine, zinc and antioxidants—Pressure Injury Stage 2 or greater2
Support Resources
You must be logged in to view all resources.
5 Evidence Found
14 Tools and Product Support Found
7 Patient Resources Found
5 Videos
References
1. Padula, W., Delarmente, B. A. (2019). The national cost of hospital-acquired pressure injuries in the United States. International Wound Journal. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.1307
2. EPUAP, NPIAP & PPPIA. Prevention and Treatment Pressure Ulcers/Injuries: Quick Reference Guide. Emily Haesler (Ed.). EPUAP/NPIAP/PPPIA: 2019.