Wound Management
Impact on Outcomes and Cost of Care
Non-healing wounds cost the US Healthcare system an estimated $50 Billion per year.1
- The average cost to heal a wound is $39271
- In patients with two or more comorbidities, the average cost to heal increases to $42821
- Patients with comorbidities (i.e. diabetes, obesity), older patients and those with malnutrition are at greater risk for developing wounds1,2
Distribution by Wound Type1
- Surgical Wounds 20.8%
- Traumatic Wounds 12.8%
- Pressure Injuries 19.2%
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer 13.7%
- Chronic Ulcer 12.1%
Value of Nutrition Intervention
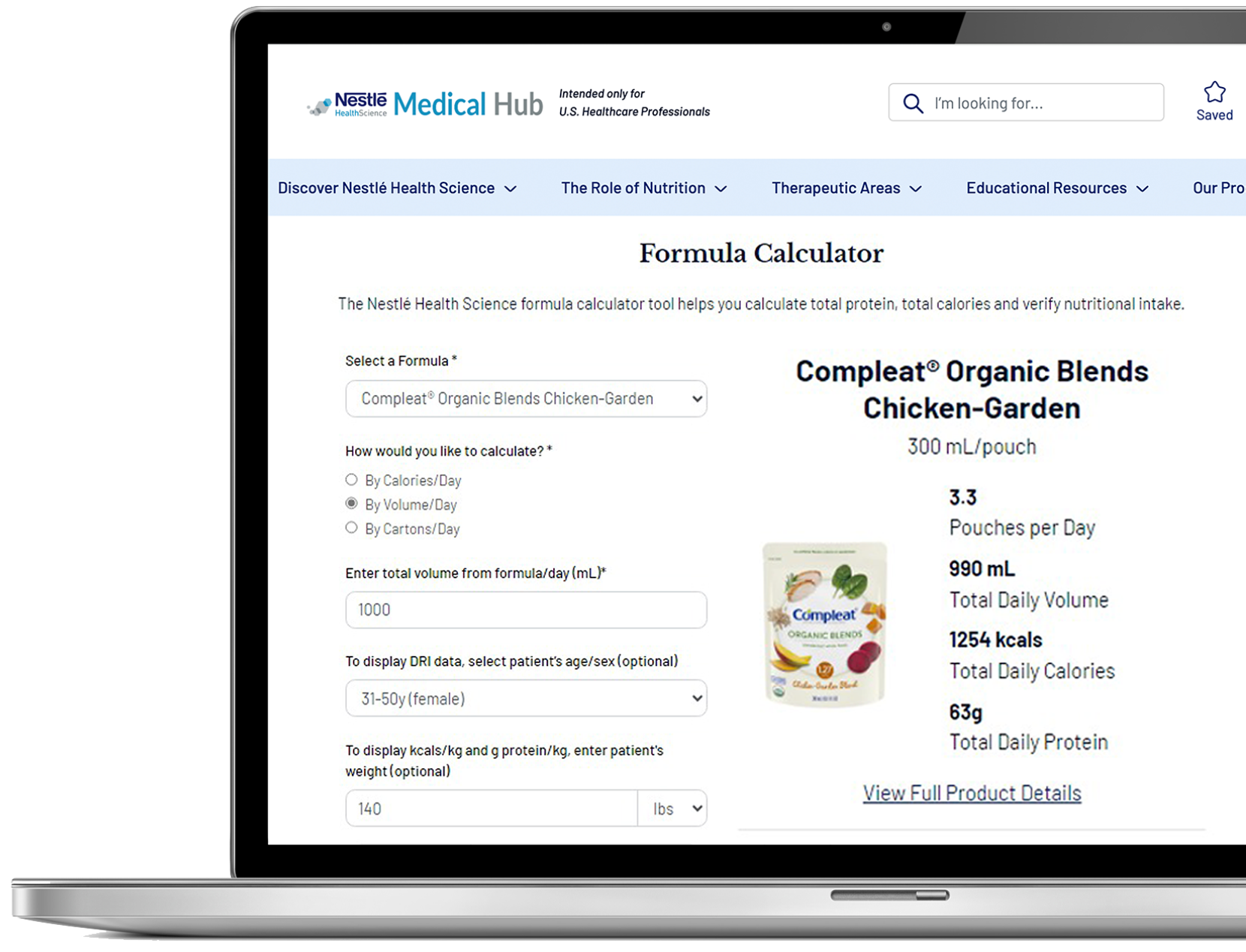
The process of wound healing is metabolically demanding. Give your patients with partial or full thickness wounds the specialized nutrition they need.
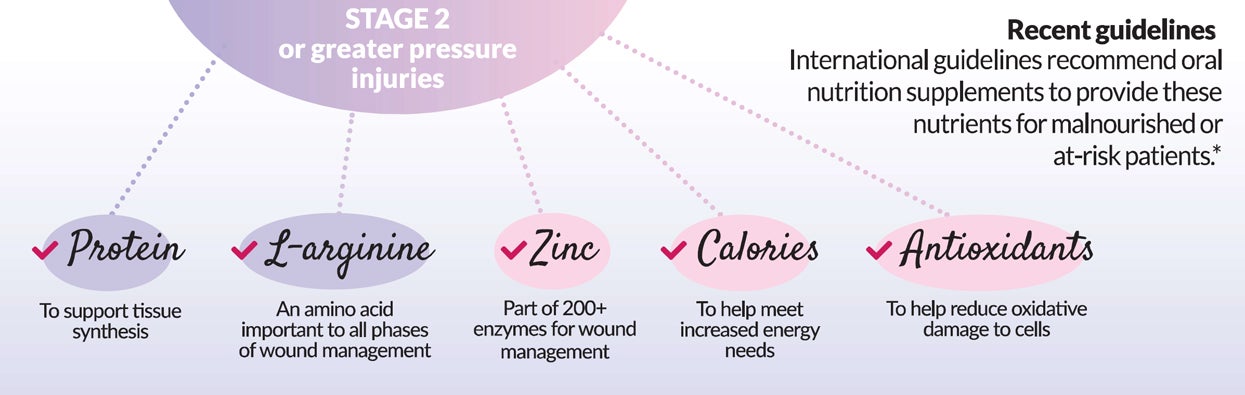
In malnourished or at risk patients with Stage 2 or greater pressure injuries, international guidelines recommend oral nutrition supplements to provide these key nutrients*:3
- Protein: to support tissue synthesis
- L-arginine: an amino acide important to all phases of wound management
- Zinc: part of 200+ enzymes for wound management
- Calories: to help meet energy needs
- Antioxidants: to help reduce damage to cells
Nestlé Health Science offers two options to support the nutritional needs of patients with partial and full thickness wounds including pressure injuries, surgical wounds, diabetic foot ulcers, vascular ulcers and more:

IMPACT Advanced Recovery® Drink
Provides very high protein, calories and L-arginine in a single product. Case studies show sustained compliance and improved wound management with a 30-day protocol.4-5
Learn More about IMPACT Advanced Recovery® Drink and improved outcomes in Surgical patients.
Medicare Advantage Plans
What if, with one simple evidence-based change, you could:
- Support wound management3,6-9
- Achieve better outcomes10-16
- Lower overall cost of care6,17-20
Malnourished patients have higher rates of impaired wound healing. Nutrition intervention helps to:21
- Reduce hospital readmissions6
- Reduce the risk of infections22
Tools & Resources
Access Nestlé's evidence-based protocols, tools and products to help lower total cost of care and improve outcomes in patients with wounds.
Contact Us
Contact Us now to learn more about reducing total cost of care and improving clinical outcomes with our expansive portfolio of nutrition products.
Please include your first and last name, email address, phone number, company, and title in your email.
References
1. Fife CE, et al. Wound 2012;24(1):10-17.
2. Sen CK, et al. Wound Repair Regen 2009;17(6):763-771
3. EPUAP, NPIAP & PPPIA. Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries : Quick Reference Guide Emily Haesler (Ed.). EPUAP/NPIAP/PPPIA:2019.
4. Miranowski MK, et al. Case study: High Protein Immunonutrition Supplement Supports Limb Salvage. Presented at WHS/SAWC 2022, Phoenix AZ: P31.
5. Miranowski MK, et al. Case study: Nutritional Supplements Support Limb Salvage from Chronic Leg Ulcer Due to Pyoderma Gangrenosum. Presented at WHS/SAWC 2022, Phoenix, AZ: P30.
6. Farreras N, et al. Clin Nutr 2005;24:55-65.
7. National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance. Cambridge Media, 2014.
8. Stratton RJ et al. Ageing Res Rev. 2005;4:422-450.
9. Collins CE et al. Nutrition. 2005;21:147-155.
10. Banerjee S, et al. Nutr 2017;42:106-113.
11. Cawood AL et al. Ageing Res Rev. 2012;11:278-296
12. Persson M et al. Clin Nutr. 2007;26:216-224.
13. Rabadi MH et al. Neurology. 2008;71:1856-1861.
14. Norman K et al. Clin Nutr. 2008;27:48-56.
15. Chapman IM et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89:880-889.
16. Neelemaat F et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60:691-699
17. Sulo S et al. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2017;10:262-270.
18. Philipson TJ et al. Am J Manag Care. 2013;19:121-128.
19. Elia M et al. Clin Nutr. 2016;35:125-137.
20. Arnaud-Battandier F et al. Clin Nutr. 2004;23:1096-1103
21. Tappenden KA, et al. J Acad Nutr Diet 2013;113:1219-1237
22. Elia M et al. Clin Nutr. 2016;35:370-380
*This statement does not constitute an endorsement of IMPACT(R) formula or any other Nestlé Health Science Product by NPIAP, EPUAP or PPPIA.
**Arginaid and IMPACT Advanced Recovery are intended for use under medical supervision.