FOR YOUR GI IMPAIRED PEDIATRIC PATIENTS
whey better
nutrition starts with

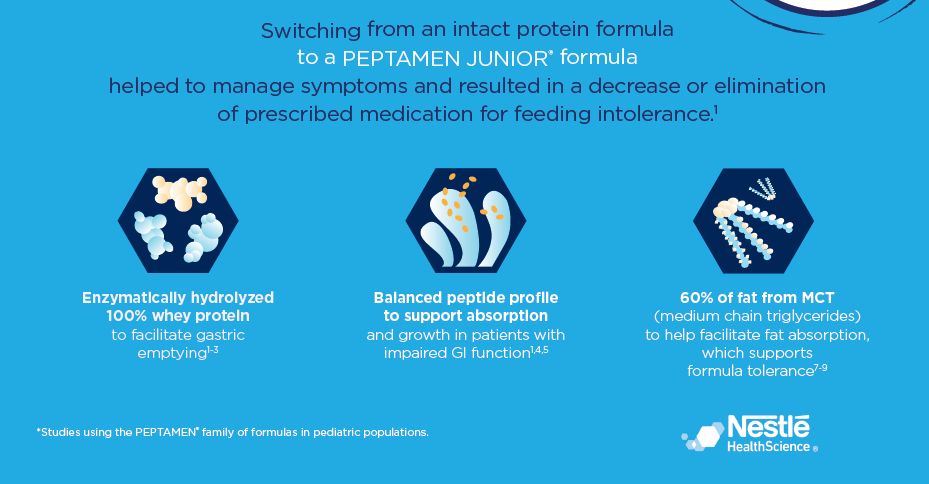
Better GI Tolerance is associated with use of
PEPTAMEN JUNIOR® formulas in pediatric patients with GERD and gastroparesis.
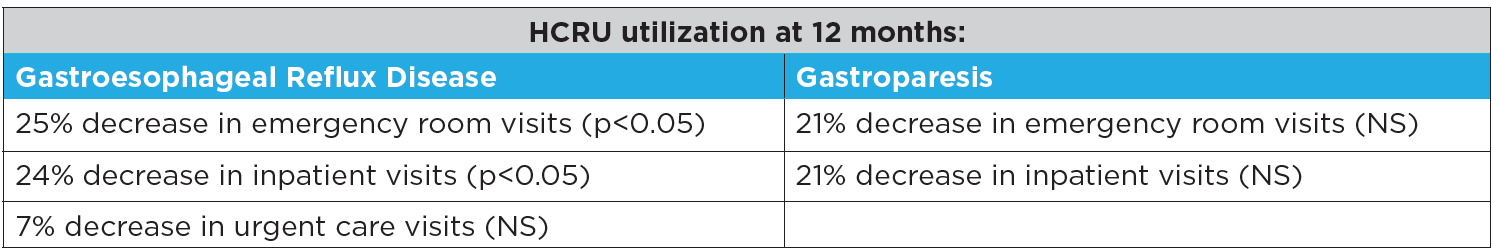
Additionally, pediatric patients with GERD and gastroparesis
who received PEPTAMEN JUNIOR® formulas had significant reductions in Healthcare Resource Utilization costs.
Additionally, pediatric patients with GERD and gastroparesis who received PEPTAMEN JUNIOR® formulas had significant reductions in Healthcare Resource Utilization costs.
Abstract Study Summary
Gastrointestinal Intolerance and Healthcare Resource Utilization in Children with Motility Disorders Receiving a Whey Peptide-Based Enteral Formula in Post-Acute Care: A Retrospective Analysis
Background
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and gastroparesis (GP) are some of the most common gastrointestinal (GI) disorders in children. These disorders are characterized by physical symptoms that lead to inadequate nutritional intake with potential for malnutrition and its ramifications.
Objective
Assess GI intolerance symptoms and healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) in children with GERD and/or GP who have been prescribed a 100% whey, peptide-based formula (w-PBF) enteral feeding in the post-acute care setting.
Methods
This was a retrospective analysis of de-identified medical claims data from the Decision Resources Group Real World Evidence Data Repository (Jan 2013-July 2023) evaluating children (≥ 1 to <18 years) fed with a Peptamen Junior® formula [w-PBF] for ≥7 consecutive days in post-acute care. Pre- and post-index periods were defined as 1 year before the first w-PBF and up to 12 months following (post-index) the first w-PBF claim date, respectively. Study periods were 1-, 3-, 6- and 12 months post-index. Intolerance symptoms noted were abdominal distention and pain, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, gagging and retching, and nausea and vomiting.
Results
1019 patient with GERD (mean age 5.2 years) and 113 with gastroparesis (mean age 7.6 years) were assessed. The mean Pediatric Comorbidity Index (PCI) score was 7.5 in those with GERD and 7.9 in those with GP. At 12 months post-index, there were significant decreases in GI intolerance symptoms of abdominal distention and pain, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea and vomiting in those children with GERD (p<0.001). Likewise, those children with GP also had significantly decreased GI symptoms of abdominal distention, flatulence, nausea and vomiting at 12 months post-index (p<0.02)
Conclusions
■ The use of w-PBF in children with GERD or GP was associated with significant reductions in GI intolerance symptoms and HCRU within the 12-month post-index period.
■ This data supports the use of Peptamen Junior® formulas in children with GI motility disorders who require enteral nutrition support in post-acute care.

Better GI Tolerance is associated with use of
PEPTAMEN JUNIOR® formulas in pediatric patients with GERD and gastroparesis.
At 12 months post-index, the use of PEPTAMEN JUNIOR® formulas in pediatric patients with GERD
was associated with:

48% decrease in Abdominal Distention

45% decrease in Flatulence

37% decrease in Nausea & Vomiting

30% decrease in Abdominal Pain

27% decrease in Diarrhea
At 12 months post-index, the use of PEPTAMEN JUNIOR® formulas in pediatric patients with gastroparesis was associated with:

57% decrease in Abdominal Distention

55% decrease in Flatulence

28% decrease in Nausea & Vomiting
To request samples and find out more information contact your Nestlé Health Science representative, call 1-800-422-ASK2 (2752), or visit www.NestleMedicalHub.com/brands/peptamen.
Helpful Links:
Download the PDF version of this Peptamen Power Pack
Study Abstract: Gastroenterology - Search Results (gastrojournal.org)
The poster presented at Digestive Disease Week may be accessed online: Use of Peptamen Junior formulas in children with gastric motility disorders | Nestlé Medical Hub (nestlemedicalhub.com)
*Nestlé Health Science employee.
All trademarks are owned by Société des Produits Nestlé S.A., Vevey, Switzerland.
©2025 Nestlé. All rights reserved.